
Burning of Baton Rouge
"Banks's Expedition- burning of the state capitol of Louisiana, Baton Rouge, Tuesday night, December…

War in Louisiana
"The war in Louisiana. The army of General Banks crossing Vermilion Bayou, October 10th, 1863. Our artist…
War in Texas
"The War in Texas. Brownsville, occupied by the army under Major General N. P. Banks, in 1863. The sudden…

War in Louisiana
"The war in Louisiana. General Banks's army, in the advance on Shreveport, crossing Cane River, March…
!["Assault of the Second Louisiana [African American] Regiment on the Confederate works at Fort Hudson, May 27th, 1863. The Battle of Fort Hudson was a severe and well-fought action. The Federal troops displayed their usual bravery, and were well handled by General Banks, driving the enemy to his second line of works. Of the [African American] regiments General Banks, in his official report, says: 'They answered every expectation. Their conduct was heroic. No troops could be more determined or more daring. They made during the day three charges upon the batteries of the enemy, suffering very heavy losses, and holding their position at nightfall with the other troops on the right of our line. The highest commendation is bestowed upon them by all officers in command on the right. Whatever doubt may have existed heretofore as to the efficiency of organizations of this character, the history of this day proves conclusively to those who were in a condition to observe the conduct of these regiments that the Government will find in this class of troops effective supporters and defenders. The severe test to which they were subjected, and the determined manner with which they encountered the enemy leave upon my mind no doubt of their ultimate success. They require only good officers, commands of limited numbers, and careful discipline to make them excellent soldiers.'"— Frank Leslie, 1896](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/11800/11805/ft-hudson_11805_mth.gif)
Fort Hudson
"Assault of the Second Louisiana [African American] Regiment on the Confederate works at Fort Hudson,…

Kirby Smith
"Voluntary dispersion of Kirby Smith's Confederate army at Shreveport, La., May 23rd, 1865. There was…

War in Louisiana
"The war in Louisiana- Battle of Mansfield, between General Banks and General Dick Taylor, April 8th,…

Battle of Grand Coteau
"The war in Louisiana- Battle of Grand Coteau- capture of the Sixty-seventh Indiana by the Texas Mounted…

Lafayette Parish
"The war in Louisiana- General Franklin's army crossing the prairie in Lafayette Parish, November 16th,…

Battle of Belmont
"Battle of Belmont, Mo., opposite Columbus, Ky, November 7th, 1861- Federal forces commanded by U. S.…

Blue-Winged Yellow Warbler
Found from Louisiana to New Jersey, the blue-winged yellow warbler migrates south to tropical parts…
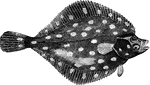
Plaice
"Weighing six to twelve pounds; it feeds on mollusca, crustacea, and young fish; inhabits sandy banks…

Penn's seal and signature
"Penn's Seal and Signature. This is a representation of the seal and signature of William Penn attached…

William Tryon Seal
"Seal and signature of Tryon. William Tryon was a native of Ireland, and was educated to the profession…

William the Conqueror
"William the Conqueror (1066-1087), as represented on his seal. Although William really ruled 'as king…

Eagle on Seal of United States
"The Eagle is a gold coin of the United States, value $10; half-eagle, $5; quarter-eagle, $2.50, double…

Hooded Seal
"The Seal, of the family Phocidæ, or seal tribe, are, of all four-limbed mammiferous animals,…
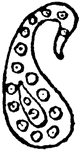
Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…

Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…
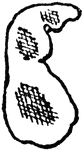
Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…

Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…
Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…
Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…
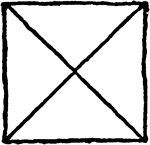
Solomon's Seal
Built on the right angle triangle and, like the Signet of David, it is found in many of the Turkish…

Seal
The general name of certain genera of carnivorous mammals, havin feet adapted for swimming, and being…
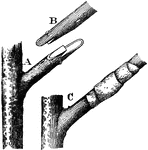
Tongue Grafting
To graft two plants together using the tongue or whip grafting approach, you must first make a sloping…

































